|
M u s c l e s |
|---|
What's the big idea?
Muscles are deformation controls made out of bones (and they
look the same as bones except that they are blue). One
difference between Muscle Bones and real
bones is that real bones cause the
movement of bones, whereas with Muscle
Bones, it's the bones they're connected to that cause the
movement. Visually, the results are the same.
The Muscle works by defining a connection point (or "target"), usually a null or another bone. This connection point and the pivot point of the Muscle itself can be thought of as the tendons connecting a muscle to two bones. When these two points move closer together the muscle bone scales and rotates to stay in contact with the connection object. So there.
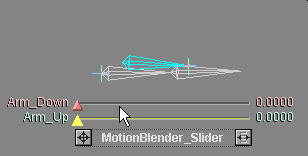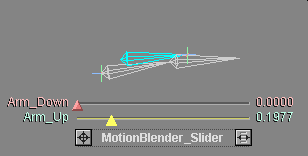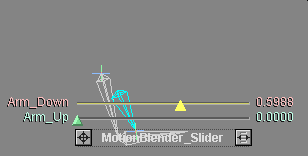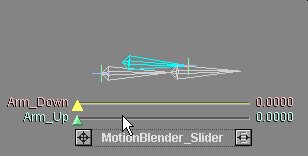
The blue bone in this animation is a muscle.
How to add
muscle--without breaking a sweat:
Besides the FlexMotion method (see bottom of page), muscles
can be created in a few ways:
-
By simply creating the bone as a muscle in the first place. This is done on the Bone block. Turn on the Muscle Bone button, then create the bone.
-
By turning on the Muscle Bone button on the Bone block in Setup.
-
By applying the Muscle function (as an expression) on the Command tab. Click on New Variable on the Variables block, then select Muscle in the Function pulldown list on the Expression block. There are four function arguments to fill in:
-
The bone (or other object) that you want to be a muscle.
-
The item (usually a null object) that you want the muscle's end to stick to. The muscle will stretch between it's 0 point (the point at the fat end) and this item. So if it were a muscle for the thigh, the 0 point (fat end-- pun fully intended) would be at the pelvis, and the "End of muscle connection" would be a null object placed at the knee.
-
Tension: sets the tension of the muscle at its default position. In other words, at its default position, is it taut and flat or bulged? Note: This parameter is not active yet.
-
Contraction: sets how the muscle maintains its volume; does it not have much difference between relaxed and contracted, or does it make a "big muscle". Note: This parameter is not active yet.
-
When you're finished with the arguments, click on the little gray box to the right of the Function pulldown list. That will apply the expression.
-
Helpful hints and information:
Muscles can also be made with the Squash & Stretch
feature of FlexMotion. Just set up the bones and apply
a FlexMotion curve, then set the Match Curve to
Absolute Length or Uniform Curve Segments, turn on
Scale Children Xform, and set the Elasticity to
Squash & Stretch. This type of muscle is
especially useful for things like mouths and eyebrows.
Additional Information: Bone block Muscle Bone Tutorial